Diabetes Mellitus and Periodontal Disease: A Pilot Investigation Into Patient Awareness Of Glycated Haemoglobin Levels And Periodontal Screening Scores And Their Associated Risk Factors In General Dental Practice
Stephen J Goode1, Christopher Turner2*.
1 General Dental Practitioner, Cirencester, UK.
2 Specialist in Restorative Dentistry (Rtd), Bath, UK.
*Corresponding Author
Christopher Turner. MSc, BDS, MDS, FDSRCS, FCG Dent,
Specialist in Restorative Dentistry (Rtd), Bath, UK.
Email Id: info@spacemark-d.com
Received: July 30, 2024; Accepted: August 12, 2024; Published: August 17, 2024
Citation: Stephen J Goode, Christopher Turner. Diabetes Mellitus and Periodontal Disease: A Pilot Investigation Into Patient Awareness Of Glycated Haemoglobin Levels And Periodontal
Screening Scores And Their Associated Risk Factors In General Dental Practice. Int J Diabetol Vasc Dis Res. 2024;11(01):287-290.
Copyright: Christopher Turner©2024. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Abstract
The two-way inter-relationship between diabetes mellitus and periodontitis, with each disease affecting the other and vice
versa, is well established, although the cause is still under investigation and may be related to chronic infection.
People living with diabetes are at 3 to 4 times higher risk of developing periodontitis than non-diabetics, rising to 10 times if
they smoke. When periodontitis is controlled, there is an improvement in glycaemic control. However, doctors and dentists
may not be sharing their screening results with each other and with their patients despite recent calls for better interprofessional
working.
Dentists and their teams should review their medical history forms to include a question about their patients' glycated haemoglobin
level, as this is a risk factor for the progression of both medical and dental complications associated with diabetes
mellitus.
The present pilot study investigated patients' knowledge of their glycated haemoglobin levels, if known, and reviewed their
dental status using Basic Periodontal Examination scores, the UK equivalent of CPITN.
2.Philosophy and Discussion
3.Conclusion
4.Acknowledgement
5.References
Keywords
Diabetes; Periodontitis; Risk Assessment; Medical History.
Introduction
The relationship between diabetes mellitus (DM) and periodontitis
(PD) is well established as a bidirectional interaction [1]. The
diseases are linked, although the pathophysiological mechanism
of the relationship is still under investigation [2]. There is a common
pathogenesis. This is caused by the chronic effects of hyperglycaemia
involving an enhanced inflammatory response at both
local and systemic levels [3]. Toxic products from gram-negative
organisms in mature plaque stimulate an inflammatory response
in the periodontium. It is the severity of the hyperglycaemia that
affects the periodontium most [4].
People with DM have a three to four times greater risk of developing
PD than non-diabetics, rising to ten times greater for
smokers [5].
In the UK in 2022, The National Institute for Clinical Excellence
(NICE) recommended medical practitioners to advise their patients
with diabetes mellitus that they are at greater risk of developing
periodontitis than non-diabetics and that successful periodontal
maintenance improves glycaemic control [6, 7].
There have been calls for better interprofessional education and
collaboration between doctors and dentists to provide more seamless
healthcare for these patients [8, 9]. Both parties must know
their screening results and how risks can be quantified. These
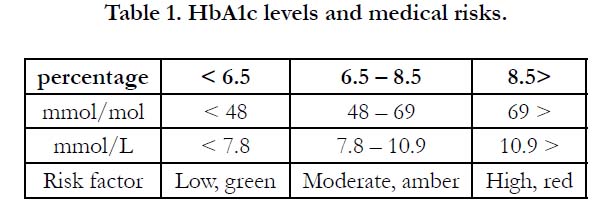
risks have been associated with HbA1c glycated haemoglobin levels
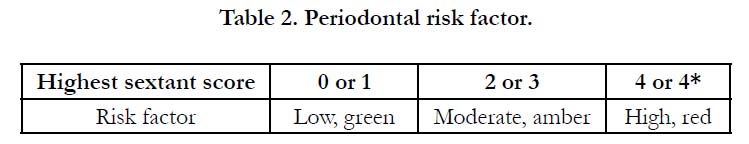
for medical risks (Table 1) and a Basic Periodontal Examination
(BPE), the UK version of the Community Periodontal Index of Treatment Needs (CPITN)[10] scores for dental risks (Table 2)
using a traffic light method of risk analysis [11, 12].
If more seamless care is to be achieved, dentists will need to ask
for HbA1c levels from diabetic care teams, have additional information
on their medical history forms and share their BPE results
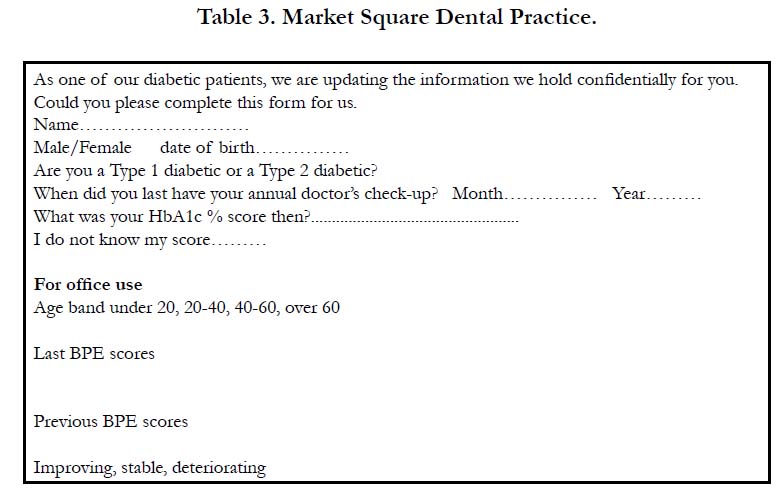
with these teams. A form has been developed for this purpose
and for patients to keep and show their respective health care
professionals [11].
Material and Methods
A pro forma (Table 3) was developed to ask patients if they
knew their HbA1c score, when they last had their annual medical
check, and whether they were type 1 or type 2 diabetics to check
against their medical risk, as determined from Table 1. Their last
two successive CPITN scores were recorded, and the highest sextant
score was taken and then compared. If there was no change
the periodontal status was considered to be stable, an increase in
score deterioration, or a decrease in the score improvement using
the criteria detailed in Table 2.
Individual oral hygiene performance and plaque control were not
reviewed.
Results
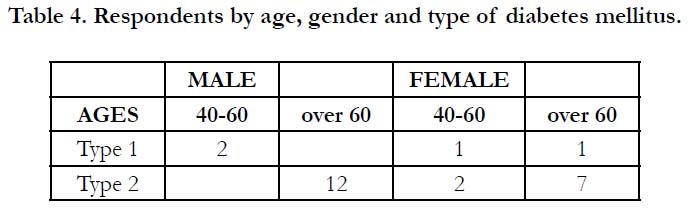
Twenty-five successive patients of SJG attending a general dental
practice in Cirencester were recruited into the study, 14 males and
11 females, and placed into age categories 20-40, 40-60, and over
60. No patients were in the 20-40 year-old group. Two 40-60 yearold
males were type 1 diabetics. For females, there was one patient
in each of the 40-60 and over 60 year-old age groups (Table 4).
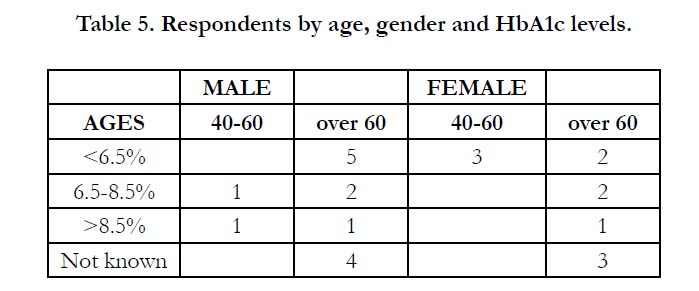
Responders recorded their HbA1c levels using either percentage
or mmol.mol scores. Four male and three female patients were
unaware of their HbA1c levels. Ten patients, five male and five
female, had scores below the ideal (green) 6.5 per cent. Two males
and two females were in the amber risk group, and two males and
one female patient were in the highest risk (red) category with
HbA1c levels greater than 8.5 per cent (Table 5). Three patients
had not had recent annual medical reviews.
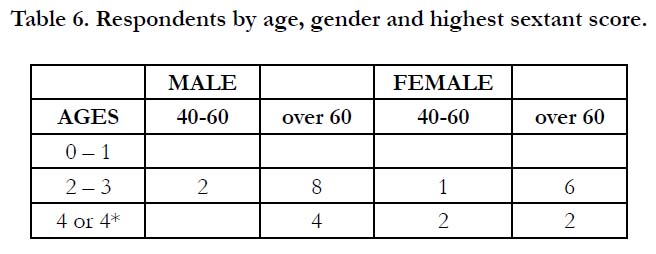
When BPE risks were assessed, none of the study group of patients had a low, green risk for periodontal disease with scores
of either 0 or 1. The majority, ten males and seven females had
scores of 2-3, amber risk, and four males and four females scored
4 or 4*, red risk (Table 6).
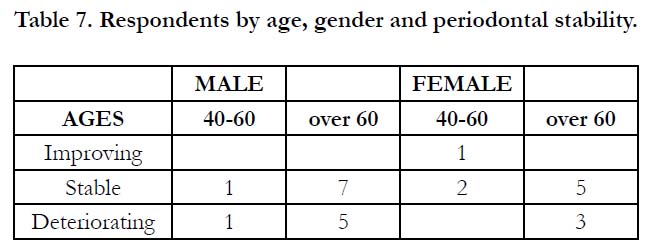
Only one female patient in the 40-60 age group had an improving
periodontal status. The majority, eight males and seven females,
were stable, and six males and three females had deteriorating
(red) periodontal status (Table 7).
This study identified one male 40-60 year-old Type 1 diabetic
with the highest (red) HbA1c risk and a deteriorating periodontal
status. One over-60-year-old female was similarly identified as at
most significant risk, and she is now deceased.
Discussion
HbA1c levels have been variously described using percentages and
mmol/mol (Table 1). The latest recommended scoring system is
mmol/L. While percentages are perhaps the easiest for patients to
understand, there is an urgent need for the medical profession to
have a single, standardised scoring method to prevent confusion
and to create a clearer picture for their dental colleagues.
Doctors and their teams need to ensure that their patients living
with diabetes have and understand the significance of their glycated
haemoglobin levels. In this study, two male and one female
patient were in the highest (red) risk group. As both medical and
dental risks have increased, it is suggested that controlling periodontal
disease in these individuals will be harder until their medical
treatment improves.
Three patients had not been attending for the recommended
regular annual medical reviews. They were advised that this is an
important part of their care and an area where medical and dental
collaboration should improve patient outcomes [8, 9]. Dentists
are encouraged to take more detailed medical histories for their
diabetic patients as part of this process [13].
Most patients, seventeen, had CPITN scores of 2-3 (amber risk)
and were considered stable. However, this category may give a
false impression about the actual periodontal status. Score 2 is
ascribed to calculus, whether supra- or sub-gingival, and score 3
to periodontal pockets of up to 5.5mm in depth. It has been proposed
that score 2 is too generalised to evaluate the significance
of calculus properly [11]. For example, a small quantity of supragingival
calculus around the lingual surfaces of lower incisor teeth
would score 2 and place a patient in a higher risk group than the
true clinical presentation would merit. Therefore, score 2 is too
wide a band and should be changed to 2, supra-gingival and 2*
subgingival calculus. The risk categories would then change to 0,
1, 2 (green, low risk), 2*, and 3 (amber risk), a truer reflection of
dental health. A revised periodontal risk form is proposed (Table
8) and is downloadable at www.chooseabrush.com.
This pilot study also suggests that it is important that people living
with diabetes have regular dental care and that this underlying
disease is making it harder to achieve periodontal control compared
with non-diabetic patients.
Conclusions
The medical profession urgently needs to standardise the HbA1c
score using one method, not three.
Patients who have not been attending for annual checks have been
identified.
As dentists ask for more information in medical histories for people
living with diabetes mellitus, they will be able to identify those
who are at greatest risk, as shown by high (red) HbA1c levels, as
they are likely to be less responsive to periodontal improvement.
Dentists need to share their CPITN results with patients as a matter
of routine and could use a previously developed pro forma
for this purpose.
To better identify periodontal risks and treatment needs, the Category
2 CPITN score should be divided into supra- and subgingival
categories.
Better information sharing between medical and dental teams requires
a paradigm shift in thinking and action.
Declaration of Interest
Dr Turner is the designer of the Chooseabrushģ method of plaque control.
References
- StŲhr J, Barbaresko J, Neuenschwander M, Schlesinger S. Bidirectional association between periodontal disease and diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Sci Rep. 2021 Jul 1; 11(1):13686. PubMed PMID: 34211029.
- Tsai C, Hayes C, Taylor GW. Glycemic control of type 2 diabetes and severe periodontal disease in the US adult population. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2002 Jun;30(3):182-92. PubMed PMID: 12000341.
- Liu R, Bal HS, Desta T, Behl Y, Graves DT. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha mediates diabetes-enhanced apoptosis of matrix-producing cells and impairs diabetic healing. Am J Pathol. 2006 Mar;168(3):757-64. PubMed PMID: 16507891.
- Genco RJ, Borgnakke WS. Risk factors for periodontal disease. Periodontol 2000. 2013 Jun;62(1):59-94. PubMed PMID: 23574464.
- Battancs E, Gheorghita D, Nyiraty S, Lengyel C, EŲrdegh G, BarŠth Z, VŠrkonyi T, Antal M. Periodontal Disease in Diabetes Mellitus: A Case- Control Study in Smokers and Non-Smokers. Diabetes Ther. 2020 Nov;11(11):2715-2728. PubMed PMID: 32975709.
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Type 1 diabetes in adults: diagnosis and management. London NICE 2022.
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Type 2 diabetes in adults: diagnosis and management. London NICE 2022.
- Siddiqi A, Zafar S, Sharma A, Quaranta A. Diabetes mellitus and periodontal disease: The call for interprofessional education and interprofessional collaborative care - A systematic review of the literature. J Interprof Care. 2022 Jan-Feb;36(1):93-101. PubMed PMID: 33290117.
- Turner CH. Diabetes mellitus and dental health: A review. Geriatric Med J. 16 November 2021. https://gm journal.co.uk/diabetes-and-dental-healtha- review.
- Barmes D. CPITN: a WHO initiative. Int Dent J 1994, 44: 523-525.
- Turner C. Diabetes mellitus and periodontal disease: the profession's choices. Br Dent J. 2022 Oct;233(7):537-538. PubMed PMID: 36241800.
- Turner C, Bouloux PM. Diabetes mellitus and periodontal disease: education, collaboration and information sharing between doctors, dentists and patients. British Journal of Diabetes. 2023 Jun 28;23(1):35-8.
- Turner CH. An updated medical history form for people living with diabetes mellitus. Br Dent J, in press.