A Retrospective Marginal Fit Evaluation Of A Fixed Dental Prosthesis Framework Fabricated By Various Dental Students
M. Sai Teja Reddy1, Nabeel Ahmed2*, Keerthi Shasanka3
1 Saveetha Dental College and Hospitals, Saveetha Institute of Medical and Technical Sciences, Saveetha University, Chennai, India.
2 Senior Lecturer, Department of Prosthodontics, Saveetha Dental College and Hospitals, Saveetha Institute of Medical and Technical Sciences, Saveetha University, Chennai, India.
3 Senior Lecturer, Department of Prosthodontics, Saveetha Dental College and Hospitals, Saveetha Institute of Medical and Technical Sciences, Saveetha University, Chennai, India.
*Corresponding Author
Dr. Nabeel Ahmed,
Senior Lecturer, Department of Prosthodontics, Saveetha Dental College and Hospitals, Saveetha Institute of Medical and Technical Sciences, Saveetha University, Chennai, India.
E-mail: nabeeln.sdc@saveetha.com
Received: October 07, 2020 Accepted: November 22, 2020; Published: November 25, 2020
Citation: M. Sai Teja Reddy, Nabeel Ahmed, Keerthi Shasanka. A Retrospective Marginal Fit Evaluation Of A Fixed Dental Prosthesis Framework Fabricated By Various Dental Students. Int J Dentistry Oral Sci. 2020;7(11):1094-1098. doi: dx.doi.org/10.19070/2377-8075-20000217
Copyright: Nabeel Ahmed© 2020. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Abstract
The aim of this study was to retrospectively evaluate the marginal fit evaluation fabricated by various dental students. A total of
570 data entries were taken, duplicate and missing entries were omitted. So a total of 60 entries were evaluated. The data was
collected from private dental records for the purpose of preservation and efficient analysis of the patients' details over a period
of one year from June, 2019 to March, 2020. The evaluation was done by radiographic evaluation and checked for horizontal and
vertical fit. The results of the study were subjected to statistical analysis. Data analysis was done using SPSS software version 23.0
Chi-square test and frequency evaluation was done to evaluate the marginal discrepancy of various teeth from the selected samples.
It was found that over contouring or under contouring was more evident in lower posterior restoration. Vertical discrepancy was
equally seen in all examined teeth. Association between the location of the teeth, horizontal fit and vertical fit was found to be
statistically not significant. (p>0.05).
2.Introduction
3.Materials and Methods
4.Results and Discussion
5.Conclusion
6.Author Contribution
7.Acknowledgements
8.References
Keywords
Marginal Adaptation; Fixed Partial Dentures; Overextended Margin; Under Extended Margins.
Introduction
An accurately/correctly fitting fixed prosthesis on the prepared
tooth is an utmost important for the long term success of the
fixed partial restoration [1]. The success of a dental restoration
is determined by 3 main factors:esthetic value, resistance to fracture,
and marginal adaptation [2-4]. The survival of the prosthesis
depends mainly on the marginal adaptation.These marginal gaps
(or) openings leads to plaque accumulation, biofilm deposition,
secondary caries or recurrent caries formation;periodontal diseases
[5, 6]. These microgaps will also lead to microleakage; increase
in cement wear. The importance of marginal adaptation
of fixed prosthodontics is to determine the minimum number of
gap measurements required to create consistent results for gap
analysis [7]. All these complications will affect the overall health
of the abutment teeth and the prosthesis [8].
Some of the factors that affect the seating of the prosthesis are
undercut in the preparation, distorted impression, distorted wax
pattern, distorted casting, over extended wax pattern, improper
extension of investment, improper burnout technique, excessive
proximal contacts and nodules on the casting.
Marginal adaptation with a gap of around 30 microns is clinically
acceptable. Normal acceptable margin is not overextended,
underextended, too thick or open. Various materials to check the
internal discrepancies are by using disclosing waxes, pressure indicating
paste, powdered spray, Elastomeric detection paste, Air
abrasion and by running a sharp explorer from the restoration to
the tooth and vice versa to check for any catch.
Many studies which involved case reports [9], surveys [10], systematic
reviews [11-13], literature reviews [14-17], In Vivo studies
[18-20], In vitro studies [21, 22] and retrospective studies [23] were
carried out by our team previously. We are currently focusing on epidemiological studies. The main objective of the study is to find
the frequency of marginal misfit in the abutments among various
sextants of the dental arch.
This retrospective study was conducted in the university setting.
Data chosen for evaluation were patients who reported to a private
dental college for any dental treatment. The details of the
patients were obtained from analysis of 86,000 patients from
June, 2019 to March, 2020 from private dental records for the
purpose of preservation and efficient analysis of the patients'
details including intraoral, extra oral pictures, radiographic images
and treatments done, which is maintained in a confidential
manner. These served as records for the retrospective study. The
study was conducted after getting ethical approval from the Institutional
Ethical Committee (Ethical approval number: SDC/
SIHEC/2020/DIASDATA/0619-0320). Cross verification was
done with the help of dental records data.Samples with improper
data and repetitions were excluded from the study. The data is
then arranged and checked for horizontal and vertical misfit of
the framework by examining the RVG.
Inclusion Criteria of the data of patients undergoing fixed dental
prosthesis treatment, patients with informed consent and patients
aged between 20 - 70 years. Excluded data were the ones without
acceptable radiograph for evaluation. Cross verification of
data for errors and measures are taken to minimise sampling bias
while double blinding the Analyser and Reviewer The internal and
external validity of the sample selected and all the samples are
selected based on simple random sample.The data was collected and entered in the MS Excel spreadsheet and tabulated. Descriptive
statistics was used to evaluate the marginal fit evaluation fabricated
by various dental students and statistics were carried out
using SPSS Software version 23.0 by IBM. Statistical tests used by
ChiSquare and Crosstabs data are evaluated.
Results And Discussion
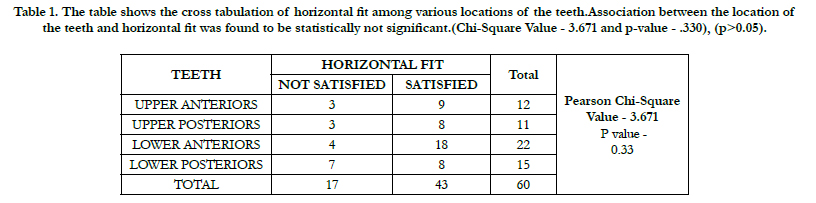
From the retrospective study, upper anteriors were reported with
a frequency of 12 out of it 9 teeth has shown a satisfactory horizontal
fit and 3 teeth has shown a not satisfactory horizontal fit,
upper posteriors were reported with a frequency of 11 out of it
8 has shown a satisfactory horizontal fit and 3 teeth has shown a
not satisfactory horizontal fit, lower anteriors were reported with
a frequency of 22 out of it 18 has shown a satisfactory horizontal
fit and 4 teeth has shown a not satisfactory horizontal fit and
upper posteriors were reported with a frequency of 15 out of
it 8 teeth has shown a satisfactory horizontal fit and 7 teeth has
shown a not satisfactory horizontal fit.(TABLE 1)
Table 1. The table shows the cross tabulation of horizontal fit among various locations of the teeth.Association between the location of the teeth and horizontal fit was found to be statistically not significant.(Chi-Square Value - 3.671 and p-value - .330), (p>0.05).
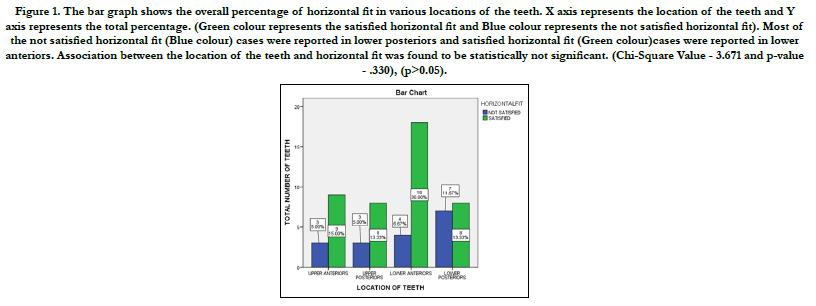
The bar graph shows the overall percentage of horizontal fit in various locations of the teeth, in upper anteriors satisfactory horizontal fit is seen in 15% and not satisfactory horizontal fit is seen in 5%,in upper posteriors, satisfactory horizontal fit is seen in 13.33% and not satisfactory horizontal fit is seen in 5%, in lower anteriors satisfactory horizontal fit is seen in 30% and not satisfactory horizontal fit is seen in 6.67% and in upper posteriors, satisfactory horizontal fit is seen in 13.33% and not satisfactory horizontal fit is seen in 11.67%. Association between the location of the teeth and horizontal fit was found to be statistically not significant.( Chi-Square Value - 3.671 and p-value - .330), (p>0.05). (FIGURE 1)
Figure 1. The bar graph shows the overall percentage of horizontal fit in various locations of the teeth. X axis represents the location of the teeth and Y axis represents the total percentage. (Green colour represents the satisfied horizontal fit and Blue colour represents the not satisfied horizontal fit). Most of the not satisfied horizontal fit (Blue colour) cases were reported in lower posteriors and satisfied horizontal fit (Green colour)cases were reported in lower anteriors. Association between the location of the teeth and horizontal fit was found to be statistically not significant. (Chi-Square Value - 3.671 and p-value - .330), (p>0.05).
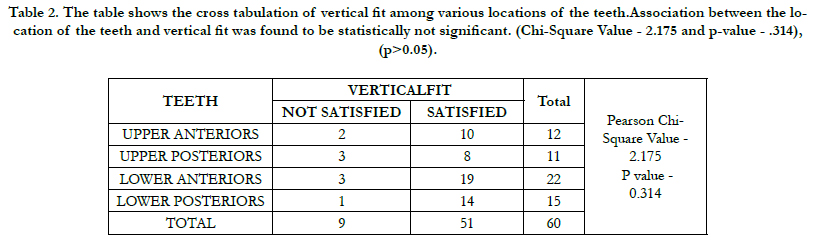
Upper anteriors were reported with a frequency of 12 out of it 10 has shown a satisfactory vertical fit and 2 teeth has shown a not satisfactory vertical fit, upper posteriors were reported with a frequency of 11 out of it 8 has shown a satisfactory vertical fit and 3 teeth has shown a not satisfactory vertical fit, lower anteriors were reported with a frequency of 22 out of it 19 has shown a satisfactory vertical fit and 3 teeth has shown a not satisfactory vertical fit and lower posteriors were reported with a frequency of 15 out of it 14 has shown a satisfactory vertical fit and 1 teeth has shown a not satisfactory vertical fit.(TABLE 2)
Table 2. The table shows the cross tabulation of vertical fit among various locations of the teeth.Association between the location of the teeth and vertical fit was found to be statistically not significant. (Chi-Square Value - 2.175 and p-value - .314), (p>0.05).
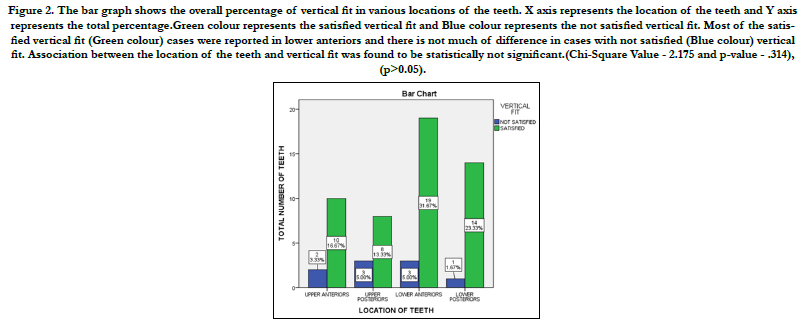
The bar graph shows the overall percentage of vertical fit in various locations of the teeth, in upper anteriors satisfactory vertical fit is seen in 10% and not satisfactory vertical fit is seen in 3.33%,in upper posteriors, satisfactory vertical fit is seen in 13.33% and not satisfactory vertical fit is seen in 5%, in lower anteriors satisfactory vertical fit is seen in 31.67% and not satisfactory vertical fit is seen in 5% and in lower posteriors, satisfactory vertical fit is seen in 23.33% and not satisfactory vertical fit is seen in 1.67%. Association between the location of the teeth and vertical fit was found to be statistically not significant (Chi-Square Value - 2.175 and p-value - .314), (p>0.05). (FIGURE 2)
Figure 2. The bar graph shows the overall percentage of vertical fit in various locations of the teeth. X axis represents the location of the teeth and Y axis represents the total percentage.Green colour represents the satisfied vertical fit and Blue colour represents the not satisfied vertical fit. Most of the satisfied vertical fit (Green colour) cases were reported in lower anteriors and there is not much of difference in cases with not satisfied (Blue colour) vertical fit. Association between the location of the teeth and vertical fit was found to be statistically not significant.(Chi-Square Value - 2.175 and p-value - .314), (p>0.05).
Marginal misfit of fixed partial dentures corresponds to the marginal gap between the edge of the prosthetic restoration and the limit of the tooth preparation [24]. It contributes to cement exposure, eventually leads to dissolution [24, 25].
Lost wax casting technique, considered the gold standard one [26]. However, it is technique sensitive; due to the possibility of distortion degree (approximately 100 microns), caused by different factors that can occur during investment; wax removal, casting, finishing and polishing for conventional casting [27]. Direct human intervention in the manufacturing of the crown could play a role according to the skill of the dental laboratory technician and the relative importance of his contribution [27, 28]. The number of steps involved in the process was another important element, because the probability of error increased with each additional step required [29].
Recently, computer aided design and manufacturing has become available increasingly. These techniques have simplified manufacturing and contributed to the use of different metals.It is reported that CAD/CAM systems, virtual design and computer controlled milling can result in better fit between the copings and the prepared tooth in comparison with the conventional method.
Jorgensen and Petersen showed that cementation could significantly compromise marginal adaptation [30]. Creating a space between the die and the prosthesis for the cement layer is known to significantly improve adaptation [31]. Eames advised coating the die, but not the marginal area, with a spacer varnish [32]. This coating is required in ceramic systems that do not involve CAD/CAM. With CAD/CAM systems, the cement space was set through the software interface. Some of the reviewed studies measured the impact of programming different settings on the resulting marginal and internal fit [33, 34].
Small cement space could lead to premature contacts between the internal surface of the crown and the abutment tooth and hinder the evacuation of excess cement from the occlusal surface of the tooth, thus widening the marginal gap [35]. In some studies the impact of porcelain veneering and firing on marginal fit was not significant [36, 37]. In contrast to this finding some authors found that porcelain veneering substantially widened the marginal gap [38, 39].
Conclusion
Generally, marginal adaptation with a gap of around 30 microns
is clinically acceptable and it can be clinically assessed by moving
a sharp explorer from the framework to the tooth and vice versa.
From the study it can be inferred that over contouring or under
contouring was more evident in lower posterior restoration. Vertical
discrepancy was equally seen in all examined teeth. Further
studies can be done in future with large sample size and evaluating
the marginal discrepancy among different finish line configurations
and the type of final restoration material.
Acknowledgements
This research was done under the research department of
Saveetha dental College and hospitals. We sincerely provide gratitude
and are very thankful to the guide who helped in making this
study possible.
Author Contributions
First author, Dr. Sai Teja Reddy collected the raw data, performed
the analysis, intercepted and wrote the manuscript. Second author,
Dr Nabeel Ahmed contributed to conception , data design,
analysis interpretation and critically revised manuscripts. The
third author, Dr. Keerthi Sasanka Participated in the study revised
the manuscript as per guideline, alignments and formatting . All
the authors have discussed the results and contributed to the final
manuscript.
References
- Felton DA, Kanoy BE, Bayne SC, Wirthman GP. Effect of in vivo crown margin discrepancies on periodontal health. J Prosthet Dent. 1991 Mar;65(3):357-64.Pubmed PMID: 2056454.
- Björn AL, Björn H, Grkovic B. Marginal fit of restorations and its relation to periodontal bone level. II. Crowns. Odontol Revy. 1970;21(3):337-46. Pubmed PMID: 5275036.
- Gardner FM. Margins of complete crowns--literature review. J Prosthet Dent. 1982 Oct;48(4):396-400.Pubmed PMID: 6752383.
- Richter WA, Ueno H. Relationship of crown margin placement to gingival inflammation. J Prosthet Dent. 1973 Aug;30(2):156-61.Pubmed PMID: 4577892.
- Groten M, Axmann D, Pröbster L, Weber H. Determination of the minimum number of marginal gap measurements required for practical in-vitro testing. J Prosthet Dent. 2000 Jan;83(1):40-9.Pubmed PMID: 10633021.
- Saltzberg DS, Ceravolo FJ, Holstein F, Groom G, Gottsegen R. Scanning electron microscope study of the junction between restorations and gingival cavosurface margins. J Prosthet Dent. 1976 Nov;36(5):517-22.Pubmed PMID: 1068287.
- Gassino G, Barone Monfrin S, Scanu M, Spina G, Preti G. Marginal adaptation of fixed prosthodontics: a new in vitro 360-degree external examination procedure. Int J Prosthodont. 2004 Mar-Apr;17(2):218-23.Pubmed PMID: 15119875.
- Cooper TM, Christensen GJ, Laswell HR, Baxter R. Effect of venting on cast gold full crowns. J Prosthet Dent. 1971 Dec;26(6):621-6.Pubmed PMID: 4941124.
- Ashok V, Nallaswamy D, Benazir Begum S, Nesappan T. Lip Bumper Prosthesis for an Acromegaly Patient: A Clinical Report. J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2014 Dec;14(Suppl 1):279-82.Pubmed PMID: 26199531.
- Ashok V, Suvitha S. Awareness of all ceramic restoration in rural population. Res J Pharm Technol. 2016;9(10):1691-3.
- Kannan A. Effect of Coated Surfaces influencing Screw Loosening in Implants: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. World J dentistry. 2017 Nov;8(6):496-502.
- Jain AR, Nallaswamy D, Ariga P, Ganapathy DM. Determination of correlation of width of maxillary anterior teeth using extraoral and intraoral factors in Indian population: A systematic review. World J Dent. 2018 Jan;9:68-75.
- Kannan A, Venugopalan S. A systematic review on the effect of use of impregnated retraction cords on gingiva. Res J Pharm Technol. 2018;11(5):2121-6.
- Venugopalan S, Ariga P, Aggarwal P, Viswanath A. Case Report: Magnetically retained silicone facial prosthesis. Niger J Clin Pract. 2014 Mar 27;17(2):260-4.
- Vijayalakshmi B, Ganapathy D. Medical management of cellulitis. Res J Pharm Technol. 2016;9(11):2067-70.
- Subasree S, Murthykumar K. Effect of Aloe Vera in Oral Health-A Review. Res J Pharm Technol. 2016;9(5):609-12.
- Selvan SR, Ganapathy D. Efficacy of fifth generation cephalosporins against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus-A review. Res J Pharm Technol. 2016;9(10):1815-8.
- Jyothi S, Robin PK, Ganapathy D. Periodontal health status of three different groups wearing temporary partial denture. Res J Pharm Technol. 2017;10(12):4339-42.
- Ranganathan H, Ganapathy DM, Jain AR. Cervical and Incisal Marginal Discrepancy in Ceramic Laminate Veneering Materials: A SEM Analysis. Contemp Clin Dent. 2017 Apr-Jun;8(2):272-278.Pubmed PMID: 28839415.
- Duraisamy R, Krishnan CS, Ramasubramanian H, Sampathkumar J, Mariappan S, Navarasampatti Sivaprakasam A. Compatibility of Nonoriginal Abutments With Implants: Evaluation of Microgap at the Implant-Abutment Interface, With Original and Nonoriginal Abutments. Implant Dent. 2019 Jun;28(3):289-295.Pubmed PMID: 31124826.
- . Ganapathy D, Sathyamoorthy A, Ranganathan H, Murthykumar K. Effect of Resin Bonded Luting Agents Influencing Marginal Discrepancy in All Ceramic Complete Veneer Crowns. J Clin Diagn Res. 2016 Dec;10(12):ZC67- ZC70.Pubmed PMID: 28209008.
- Ajay R, Suma K, Ali SA, Kumar Sivakumar JS, Rakshagan V, Devaki V, et al. Effect of Surface Modifications on the Retention of Cement-retained Implant Crowns under Fatigue Loads: An In vitro Study. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2017 Nov;9(Suppl 1):S154-S160.Pubmed PMID: 29284956.
- Basha FYS, Ganapathy D, Venugopalan S. Oral Hygiene Status among Pregnant Women. Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology 2018; 11: 3099.
- Boitelle P, Mawussi B, Tapie L, Fromentin O. A systematic review of CAD/ CAM fit restoration evaluations. J Oral Rehabil. 2014 Nov;41(11):853-74. Pubmed PMID: 24952991.
- Jei JB, Mohan J. Comparative Evaluation of Marginal Accuracy of a Cast Fixed Partial Denture Compared to Soldered Fixed Partial Denture Made of Two Different Base Metal Alloys and Casting Techniques: An In vitro Study. J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2014 Mar;14(1):104-9.Pubmed PMID: 24605006.
- Zarauz C, Valverde A, Martinez-Rus F, Hassan B, Pradies G. Clinical evaluation comparing the fit of all-ceramic crowns obtained from silicone and digital intraoral impressions. Clin Oral Investig. 2016 May 1;20(4):799-806.
- de França DG, Morais MH, das Neves FD, Carreiro AF, Barbosa GA. Precision Fit of Screw-Retained Implant-Supported Fixed Dental Prostheses Fabricated by CAD/CAM, Copy-Milling, and Conventional Methods. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2017 May/June;32(3):507–513.Pubmed PMID: 27706265.
- Pelekanos S, Koumanou M, Koutayas SO, Zinelis S, Eliades G. Micro-CT evaluation of the marginal fit of different In-Ceram alumina copings. Eur J Esthet Dent. 2009 Autumn;4(3):278-92.Pubmed PMID: 19704928.
- Syrek A, Reich G, Ranftl D, Klein C, Cerny B, Brodesser J. Clinical evaluation of all-ceramic crowns fabricated from intraoral digital impressions based on the principle of active wavefront sampling. J Dent. 2010 Jul;38(7):553-9. Pubmed PMID: 20381576.
- Jøhgensen KD, Petersen GF. The grain size of zinc phosphate cements. Acta Odontol Scand. 1963 Jan 1;21(3):255-70.
- Hollenback GM. Precision gold inlays made by a simple technic. The J Am Dent Assoc. 1943 Jan 1;30(1):99-109.
- Eames WB, O’Neal SJ, Monteiro J, Miller C, Roan JD, Cohen KS. Techniques to improve the seating of castings. J Am Dent Assoc. 1978 Mar 1;96(3):432-7.
- Nakamura T, Dei N, Kojima T, Wakabayashi K. Marginal and internal fit of Cerec 3 CAD/CAM all-ceramic crowns. Int J Prosthodont. 2003 May 1;16(3):244-248.
- Iwai T, Komine F, Kobayashi K, Saito A, Matsumura H. Influence of convergence angle and cement space on adaptation of zirconium dioxide ceramic copings. Acta Odontol Scand. 2008 Aug;66(4):214-8.Pubmed PMID: 18607834.
- Morsy ZM, Ghoneim MM, Afifi RR. INFLUENCE OF LUTING RESIN CEMENT POLYMERIZATION MODE AND VENEER THICKNESS ON THE COLOR STABILITY OF FELDSPATHIC CAD/CAM VENEERS. Alex Dent J. 2020 May 11.
- Bhowmik H, Parkhedkar R. A comparison of marginal fit of glass infiltrated alumina copings fabricated using two different techniques and the effect of firing cycles over them. J Adv Prosthodont. 2011 Dec;3(4):196-203.Pubmed PMID: 22259703.
- Pera P, Gilodi S, Bassi F, Carossa S. In vitro marginal adaptation of alumina porcelain ceramic crowns. J Prosthet Dent. 1994 Dec;72(6):585-90.Pubmed PMID: 7853254.
- Lee KB, Park CW, Kim KH, Kwon TY. Marginal and internal fit of all-ceramic crowns fabricated with two different CAD/CAM systems. Dent Mater J. 2008;27(3):422-6.
- Romeo E, Iorio M, Storelli S, Camandona M, Abati S. Marginal adaptation of full-coverage CAD/CAM restorations: in vitro study using a nondestructive method. Minerva Stomatol. 2009 Mar;58(3):61-72.Pubmed PMID: 19357612.