Myocarditis Related to Rhinovirus
Thanh DTM1*, Lien DM2, Hanh LTH2
1 General A Department of Vietnam National Hospital of Pediatrics, Vietnam.
2 Respiratory Department of Vietnam National Hospital of Pediatrics, Vietnam.
*Corresponding Author
Doan Thi Mai Thanh
General A Department of Vietnam National Hospital of Pediatrics, Vietnam.
E-mail: maithanhnhp@gmail.com
Received: November 25, 2016; Accepted: January 18, 2017; Published: January 24, 2017
Citation: Thanh DTM, Lien DM, Hanh LTH (2017) Myocarditis Related to Rhinovirus. Int J Cardiol Res. 4(1), 78-81. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.19070/2470-4563-1700013
Copyright: Thanh DTM© 2017. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Abstract
An 13 year old girl presented with chest pain, fainting and palpitations and was diagnosed with myocarditis by ECG and cardioechography. The child was treated in the ICU of the National Hospital of Pediatrics, and recovered well without complication.
2.Introduction
3.Case Presentation
4.Pre-Medical History
5. Examination
6. Investigations
7. Chest – X-ray
8.Discussion
9.Conclusion
10.Acknowledgements
11.References
KeyWords
Myocarditis; Rhinovirus; Diagnosis.
Introduction
Myocarditis has been defined by the World Health Organization/International Society and Federation of Cardiology as an inflammatory disease of the heart muscle diagnosed by established histological, immunologic, and immunohistological criteria [4]. It is a rare disease with the rate 0.5 patient per 10000 cases at the clinic [1]. It is caused primarily by numerous infectious agents, but it may also accompany autoimmune disease, hypersensitivity reactions, and toxins [2]. The core principles of treatment in myocarditis are optimal care of arrhythmia and of heart failure and, where supported by evidence, etiology-targeted therapy [3].
As myocarditis is an uncommon disease in pediatrics, we present this patient suffered from myocarditis and fully recovered without complication to share our experience in diagnosing and treating patient.
Case Presentation
A 13 years old girl presented with chest pain. 7 days before admission, the patient suffered from a mild fever, sneeze, and nasal discharge, tired and had a little cough. 3 days before admission, she had a poor appetite, felt faint and had chest pain. She was transferred to the provincial hospital, and then was diagnosed viral infection. She was treated with paracetamol, but she still felt chest pain. Therefore, she was transferred to the National Hospital of Pediatrics in the cardiology ICU with diagnosis of cardiogenic shock and suspected myocarditis.
Pre-Medical History
Normal delivery. Normal development.
Examination
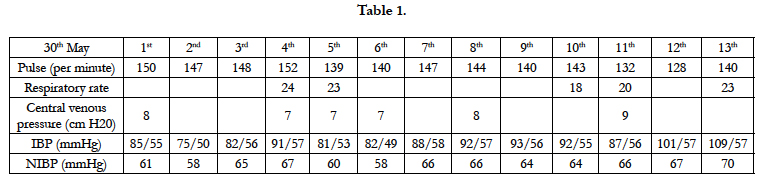
She was alert, a febrile, pallor, weal pulse and cold hands and feet. She had a little cough but no dyspnea. (Table 1)
Infectious status was unremarkable.
A cardiovascular examination: palpitation: 140 times per minute. Blood pressure: 80/50 mmHg, refill 2 second. T1, T2 were normal.
She had diminished bronchial rales in both lungs. Sp02 = 100%
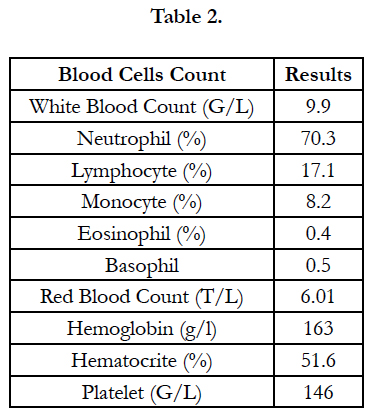
Investigations
Chest – X-ray
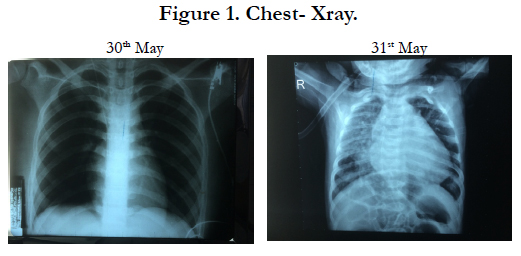
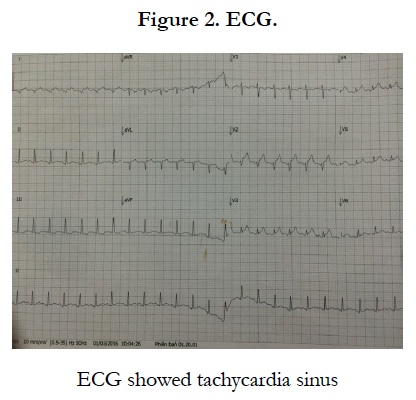
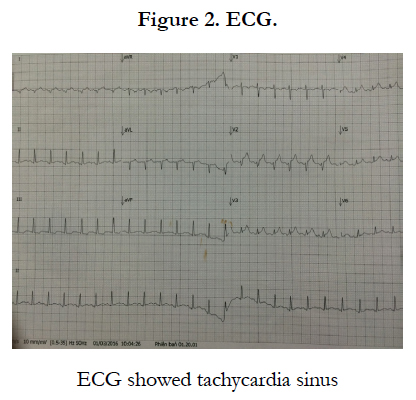
Figure 1 showed there was no change of heart’s size in chest Xray at the first day of admission.
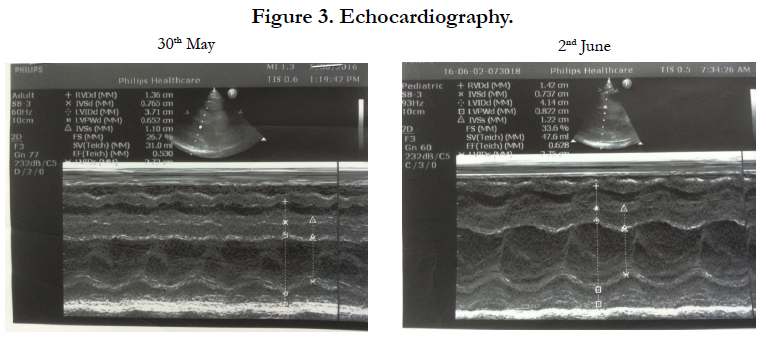
Figure 3 showed reduction of the left ventricular ejection fraction (EF = 53%) and a little pericardial effusion at the first time of admission (30th May), then the ultrasound was normal after 4 days of treatment (2nd June).
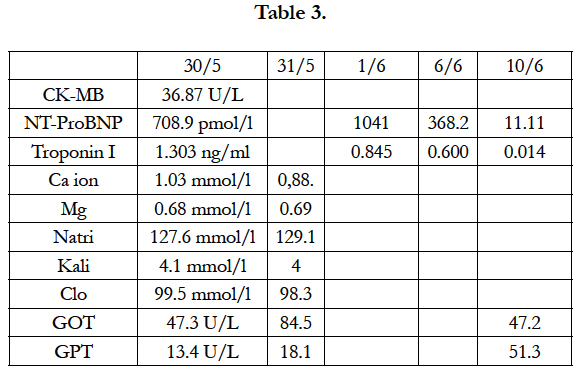
Blood test: Serum protein: 50.7g/l, Albumin: 27.3 g/l, GOT: 47.3 U/L, GPT 13.4 U/L, ure: 5.72 mmol/l, Creatinin: 63 mcmol/l, CRP: 6.82 mg/l, procalcitonin: 0.17 ng/ml. PT: 94%, APTT: 35.6 s, Fib: 4.94, INR: 1.12. Table 3.
Real time PCR Rhinovirus in the nasopharyngeal fluid: positive
Real time PCR Adenovirus in the nasopharyngeal fluid: negative
Real time PCR Enterovirus in rectal swab: negative
Bacterial culture in the nasopharyngeal fluid: negative.
Final diagnosis: Myocarditis related to Rhinovirus.
Treatment
The child was admitted to the ICU and an arterial catheter was inserted to monitor blood pressure.
The drug treatment:
1. Human Gamma globulin (High dose intravenous immunoglobulin) with dosage: 1 g/ kg of the body’s weight per day in two days (30th May and 31st May)
2. Dobutamin with dosage 7.5 mg/ kg of the body’s weight per day in the first three days (30th May, 31st May, 1st June)
3. Digoxin with dosage 0.01 mg/kg of the body’s weight in two days (31st May, 1st June).
4. Lopril, Lasix, Aldacton.
Result of treatment
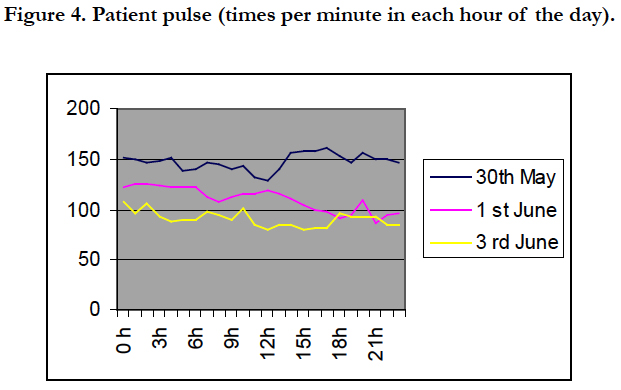
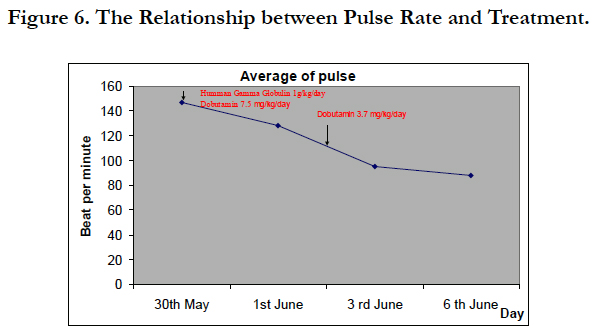
Figure 4 showed the patient’s pulse reduce to normal, from the first day of treatment (average of pulse was 147 times per minute) to the 5th day of treatment (average of pulse was 95 times per minute).
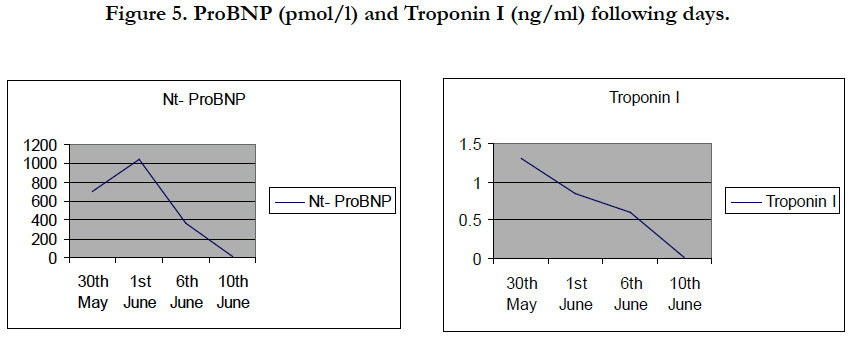
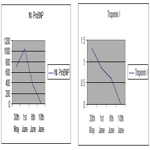
Figure 5 showed the reduction of Nt- BNP from the first day of treatment (708.9 pmol/l) to the the 12th day of treatment (11.11 pmol/l). Troponin I also reduced from 1.303 ng/ml (first day) to 0.014 ng/ml (the 12th day). Table 6.
Discussion
Myocarditis is a rare and life-threatening disease, however its signs and symptoms can overlap with other illness, for examples respiratory and gastrointestinal complaints.The causes of myocarditis are diverse and include infectious, toxic, and autoimmune etiologies. Diagnosis is difficult because there is no sensitive and specific diagnostic test for myocarditis.
In this patient, the signs and symptoms were not clear at the first time, so that the patient was misdiagnosed with myocarditis at the provincial hospital and was in severe condition (cardiac shock) at the time of admission at the National hospital of Pediatrics. The diagnosis was finally confirmed by clinical assessment (chest pain, faint, palpitation) and investigations of ECG and cardiac ultrasound and the elevation of Troponin I [3]. Although the most common causes of viral etiology are Enterovirus (coxakie virus group B) [1, 2]. We could not detect this due to the lack of the lab technique. The patient was treated and soon recovered well without complication, was followed up every 1 month at our hospital.
Conclusion
In pediatrics, myocarditis is a rare condition of which the most common causes of infectious etiologies are viruses. The spectrum of clinical symptoms varies from respiratory and cardiac complaints to gastrointestinal signs. Early diagnosis and treatment help patient recover well and reduce complications. However the child should be followed up long term with clinical assessment, ECG, echocardiography.
Acknowledgement
All authors have read and agreed to the final version of this manuscript and have equally contributed to its content and to the management of the case.
References
- http://www.uptodate.com/contents/clinical-manifestations-and-diagnosisof-myocarditis-in-children.
- Canter CE, Simpson KE (2014) Diagnosis and treatment of myocarditis in children in the current era. Circulation. 129(1): 115-28.
- http://eurheartj.oxfordjournals.org/content/34/33/2636.long
- Richardson P, McKenna W, Bristow M, Maisch B, Mautner B, et al., (1996) Report of the 1995 World Health Organization/International Society and Federation of Cardiology Task Force on the Definition and Classification of Cardiomyopathies. Circulation. 93: 841–842.