A Successful Pretreatment with Extended Corticosteroid Infusion in A Case Of an Irinotecan-Induced Hypersensitivity Reaction: Reflections On The Approach
Alketa Bakiri1, Daniela Bega2, Ervin Ç Mingomataj3*
1 American Hospital No 3, Service of Allergology& Clinical Immunology, Tirana – Albania.
2 American Hospital No 3, Service of Oncology, Tirana – Albania.
3 “Mother Theresa” School of Medicine, Department of Allergology & Clinical Immunology, Tirana - Albania.
*Corresponding Author
Ervin Ç Mingomataj,
“Mother Theresa” School of Medicine, Dept. of Allergology& Clinical Immunology, Tirana - Albania.
E-mail: allergology@gmx.de
Received: November 23, 2022; Accepted: December 13, 2022; Published: December 16, 2022
Citation: Alketa Bakiri, Daniela Bega, Ervin Ç Mingomataj. A Successful Pretreatment with Extended Corticosteroid Infusion in A Case Of an Irinotecan-Induced Hypersensitivity Reaction: Reflections On The Approach. Int J Clin Med Allergy. 2022;07(02):81-84.
Copyright: Ervin Ç Mingomataj©2022. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Abstract
The combined therapy of folinic acid, 5-fluorouracil, irinotecan, and oxaliplatin (called FOLFIRINOX) is the most effective therapy for metastatic gastrointestinal carcinomas. As a keystone of this protocol, Irinotecan rarely can induce immediate hypersensitivity reactions (HSR), which have been managed by desensitization protocols (under certain pretreatment measures). This work represents a case of an irinotecan-induced immediate HSR successfully pretreated with extended corticosteroidinfusion. Besides, it reflects on the rationality of such a therapeutic route in managing mentioned HSRs to antineoplastic drugs. This work emphasizes that a prophylactic pretreatment with extended corticosteroid infusion may suppress the HSRs occurrence, shorten the time of the treatment cycle, and avoid the need for a desensitization procedure, which in concert may lead to earlier successful completion of the antineoplastic therapy.
2.Introduction
3.Discussion
4.References
Keywords
FOLFIRINOX, Irinotecan; Metastatic Gastrointestinal Carcinomas; Immediate Hypersensitivity Reactions; Desensitization; Pretreatment; Extended Corticosteroid Infusion.
Introduction
A combination of folinic acid (leucovorin), 5-fluorouracil, irinotecan,
and oxaliplatin (called FOLFIRINOX regimen)is considered
the most effective chemotherapy for metastatic carcinomas of the
gastrointestinal system, including gastric, pancreatic, or colorectal
cancers [1-3]. Despite benefits, most neoplastic drugs cause
unpredictable immediate hypersensitivity reactions (HSR).These
reactions can affect any organ or system and range widely in clinical
severity from mild pruritus to anaphylaxis [4-7].
Moderate to severe HSRs during or after the infusion of every
key component of this first-line chemotherapeutic combination
usually needa cessation of chemotherapy or substitution of the
culprit drugto avoid more severe reactions and possible fatalities
[2-5]. The sensitivity of a tumor to certain chemotherapeutics and
the necessity to choose the most effective treatment for survival,
usually do not allow for the selection of alternative chemotherapeutic
agents [2-5, 7].
The need for first-line anticancer therapy and HSR overcoming
has been at the core of the development of varying attitudes on
the decision to rechallenge the patient after such experience, the
efficacy of desensitization protocols, and the selection and effectiveness
of drugs for premedication [2-6]. Both approaches,
the prophylactic premedication and desensitization (under certain
premedication measures) to the culprit drug are practicable options
that induce a temporary tolerance to the drug responsible
for a proven HSR [3-6, 8, 9]. While prophylactic premedication
consists of the administration of the antiallergic agent(s) before
the (first) antineoplastic medicament infusion independent of the
principal treatment, during desensitization, the principal medicament
is administered in progressively rising amounts until the
therapeutic dose is reached within a few hours [5-7]. Once a patient
completed a successful course of desensitization, all subsequent
chemotherapy courses were administered in the outpatient
facility with desensitization-trained chemotherapy personnel [5].
Being an essential component of the FOLFIRINOX combination,
irinotecan is an antineoplastic drug that prevents DNA from unwinding by inhibition of topoisomerase I [3, 4]. This agent
causes rare IgE-mediated HSRs, usually managed by rapid drug
desensitization (RDD) regimens [3]. We present the case of a
subject affected by pancreas adenocarcinoma who experienced an
IgE-mediated HSR to irinotecan and underwent a successful prophylactic
premedication with extended corticosteroid premedication
(avoiding therefore the RDD protocol). Besides, the discussion
shows a reflection on the approach.
Case Report
A54-year-old subject has been affected by locally advanced pancreas
adenocarcinoma with synchronous hepatic metastases. The
CT examination determined the diagnosis, while partial pancreatic
resection, removal of local abdominal lymph nodes, and lienfollowed
a successful chemotherapy treatment. In turn, the histopathological
examination of chirurgically-provided specimens
determined the disease’s stage (pT1N0M1). In the past, she did
experience only pruriginousurticaria 30min after penicillin or naproxen
treatment.
The neo adjuvant chemotherapy compriseda FOLFIRINOX
regimen as a first-line treatment (scheduled in six two-week cycles).
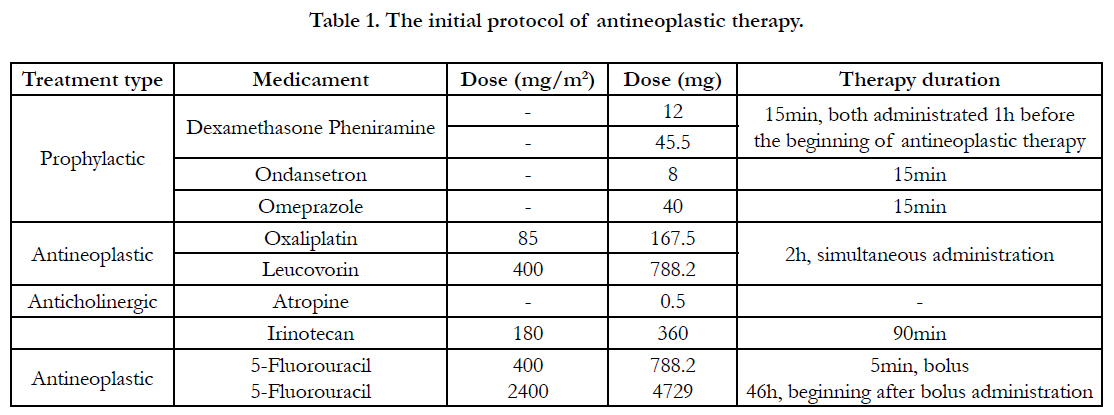
All antineoplastic drugs were infused following the oncology
department's routine administration protocol's order, dose,
and rate (Table 1). About the prophylactic drugs, dexamethasone,
pheniramine, ondansetron, and omeprazole were infused 1h before
the beginning of antineoplastic treatment, while atropine sc.
was administrated after simultaneous infusion of oxaliplatin and
leucovorin. Following product labels, the prophylactic medicaments
were applied to reduce the risk of an allergic reaction, and
adverse toxic effects of major significance (including cholinergic
acute syndrome) [6, 10].
During the firstinfusion of irinotecan alone (80 minutes after application), the patient manifested dyspnea with prominent labial and lingual angioedema (resolved with adrenaline, glucocorticoids, antihistamines, and oxygen therapy). Then, she tolerated the FOLFOX regimen, indicating an HSR towards irinotecan. Since the irinotecan was inevitable to treat the disease, the allergist proposed either a 12-step RDD protocol [11] orprophylactic pretreatment with extended corticoid doses and antihistamines 1h before the antineoplastic infusion. Given that a kind of premedication was necessary for both protocols and that the RDD protocol had to last for 6h (instead of 1.5h) [5, 11], the patient (via written consent) and oncologist approved the second alternative.
Solutions administration and patient supervision followed in an oncology service by well-trained staff. Thus, the subject received a second dose of irinotecan at a slower infusion rate preceded by the pretreatment with an extra doseof methylprednisolone 40mg iv. The subject reported light angioedema in the same corporal regions (resolved byfurther 40mg methylprednisolone). Next, a prophylactic dose of 80mg methylprednisolone iv. (collectively with dexamethasone, a dose equal to 180mg prednisolone), and 10mg of cetirizine preceded the third dose of irinotecan. This time, the pretreatment procedure was successful and the patient tolerated three additional immunotherapy cycles using this regimen without HSR episodes.
Discussion
Every infusional chemotherapy agent can cause HSRs and those
reactions have limited their use since a further application can induce
a more severe reaction and possibly death [5, 12]. The HSRs
reach a frequency of 5-27% for platins, 10-30% for taxanes, 0.6-
10% for specific monoclonal antibodies, etc. [3, 13]. According
to Çakmak et al., about 14% of patients experience HSRs during
the first chemotherapeutic cycle [7]. Yet, the HSRs of irinotecan
are less frequently observed, affecting less than 6% of treated
patients [3, 14].
Under prophylactic protocols, irinotecan RDD has been successfully
considered even after severe HSRs when substituting another
antineoplastic drug was not feasible [3, 4, 7]. The prophylactic
pretreatment comprises ondansetron, antihistamines, and 12mg
dexamethasone, which precede the 12-step RDD protocol [2, 4,
8, 11]. In this context, rechallenging the patient can be considered
an option only after the symptoms have completely resolved [2,
15].
Despite the induction of a temporary toleration state and the accompanying
premedication, the occurrence of breakthrough adverse
reactions (BTRs) during RDD with various antineoplastic
agents isobserved in 10-40% of cases [11, 16], and their severity is
significantly associated with initial HSR severity, history of drug
allergy, and previous exposure to chemotherapeutic agents [3]. It
is estimated that 1.3% to 3% of the RDD protocols are not completed
because of anaphylactic reactions [7, 16]. About irinotecan,
only three cases of RDD are described without any reaction
during the protocol, all of them under antiallergic pretreatment measures [3, 4].
The prophylactic pretreatment protocols may comprise the administration
of different histamine H1 and H2 receptor blockers,
glucocorticoids, montelukast, and acetylsalicylic acid on the day(s)
before and during the RDD [3-5, 16]. These protocols differ only
in terms of premedication; in the first case, it consists only of antihistamine
therapy with or without corticosteroids, while, in the
second one, the pretreatment includes the oral intake of 500mg
acetylsalicylic acid and 10mg montelukast [3, 4]. Of key importance,
the post hoc analysis did not identify any impact of the type
of premedication on the treatment efficacy on progression-free
survival and overall survival times [6]. About the first approach,
the incidence of HSRs was lower in the group of patients who
received antihistamine plus corticosteroid (9.6%) compared with
those who received antihistamine alone (25.6%). A similar trend
was seen for grade 3 or 4 HSRs (1.0% for any antihistamine plus
corticosteroid vs. 4.7% for patients receiving antihistamine alone)
[6]. Coinfusion of dexamethasone with oxaliplatin also is considered
to effectively reduce relative HSRs [2, 17]. According to literature
reports, the latter approach reduces the BTRs occurrence in
comparison to methylprednisolone pretreatment, which suggests
the involvement of prostaglandins D2 and leukotrienes in mast
cell activation [3, 18]. Yet, Cubero et al. share the opinion that
premedication with antihistamines and corticosteroids should be
only used in patients who develop repeated HSRs during previous
RDD attempts that were preceded by the pretreatment with
acetylsalicylic acid and montelukast [4].
In a few cases of antineoplastic therapy, the lack of supplemental
pretreatment with (extended) corticosteroid in fusions may lead
to unfortunate outcomes, such as refusion of 20-step irinotecan
RDD after anaphylactic reaction during the 12 and 16-step ones
[3], unfatal cardiorespiratory arrests after oxaliplatin [2, 19], and
death after cetuximab treatments [6, 20]. In fact, corticosteroids
play a secondary role in the acute phase of anaphylaxis due to
their comparatively slow onset of action [21, 22]. Their therapeutic
dose varies between 1 and 2mg/kg body weight (BW) for prednisolone
to 0.15-0.2mg/kg BW for dexamethasone. Different reviews
postulate a non-specific membrane-stabilizing effect within
10–30min of administration of very high corticosteroid doses
(in adults, 500–1000mg independent of the substance potency)
[21-23]. However, different observations demonstrate that platinderivates
cause HSRs despite the standard pretreatment (12mg
dexamethasone and antihistamines) before the RDD procedure
[2, 24]. While extended steroid premedication even avoided the
severe HSRs, allergic symptoms returned in the following cycle
when the subject did not receive corticosteroid therapy [2, 25, 26].
These findings show that, together with antihistamines, the extensive
steroid infusions on the day of the RDD procedure [dexamethasone
up to 0.3mg/kg BW or methyl (prednisolone) up to
2mg/kg BW] can be employed for safety in patients after (severe)
HSRs [2, 4]. Like our case, Thomas et al. support the opinion
that patients who develop mild to moderate allergic and infusional
reactions can be rechallenged safely after pretreatment with such
steroid infusions and antihistamines without an RDD procedure
[24].
Collectively, the need for shorter RDD protocols [7, 16, 27], being
the pretreatment with 12mg dexamethasone an integral part
of RDD [2-5, 8], the HSRs occurrence during the RDD despite
sucha pretreatment in a large proportion of the affected subjects
[3, 11, 16], and the possibility to administrate very high corticosteroid
doses during any severe HSR as reported by Ring et al. [21],
may suggest us the direct prophylactic administration of methyl
(prednisolone) up to 3-4mg/kg BW in case of severe HSRs to any
FOLFIRINOX component (Mueller: grade III-IV [28], Ring &
Messmer: grade II-IV [29], or Bakiri & Mingomataj: grade IIIAIV
[30, 31]]) skipping the antecedent introduction of an RDD
protocol. Some authors, like Bano, Nisi, and their relative collaborators
support such a courageous therapeutic route, affirming
that an extended corticosteroid premedication with slower oxaliplatin
infusion can be employed for safety in patients in cases of
severe HSR to oxaliplatin [2, 25]. The quite shorter or avoidance
of RDD protocols may allow the use of methyl (prednisolone)
as a pretreatment agent, which shows a shorter suppressive effect
on the cortex of the adrenal gland. In contrast, the quite longer
RDD protocols developed by Castells et al. [11] need the pretreatment
with dexamethasone because of the longer plasmatic
half-life [32]. In our allergological experience, the casuistic use of
methylprednisolone 3-4mg/kg BW together with antihistamines
and gastric protectors has prevented the occurrence of any immediate
BRT during the single application of medical agents like
radio contrast media, etc., despite experiencing severe HSRs in
the previous exposures (data not shown).
Conclusion
Albeit in a small number of patients, it is a pity that the oncologist
teams are constricted to stop any component of the FOLFIRINOX
regimen after any BRT occurred during the RDD
(despite the respective prophylactic therapy). Our case shows
that implementing a pragmatic and promising approach to prophylactic
premedication with both antihistamines and corticosteroids
may suppress the HSRs occurrence, shorten the time of the
treatment cycle, and avoid the need for RDD, which in concert
may lead to earlier successful completion of the FOLFIRINOX
therapy. Consequently, collaboration between oncologists and allergists
in assessing and managing HSRs, RDD, and pretreatments
is necessary to prevent discontinuing any chemotherapeutic drug.
Indeed, any of mentioned protocols should be always evaluated
as an individualized possible therapeutic route in subjects with
HSRs. Additionally, the mentioned professional staff should perform
and supervise the respective procedures in a specialized and
safe setting. Still, more prospective randomized studies are necessary
to propose individualized pretreatments and RDD protocols
in accordance with patient-specific risk stratification. At least
the investigation of whether particular corticosteroids might be
more effective than others in reducing the incidence of any FOLFIRINOX-
associated HSRs would be feasible.
Authors’ Contributionn
AB and DB managed the patient from the allergological and the
oncological point-of-view, respectively; both authors also contributed
with helpful discussions. EÇM ideated and drafted the
manuscript.
References
- Calvo E, Cortés J, Rodríguez J, Fernández-Hidalgo O, Rebollo J, Martín-Algarra S, et al. Irinotecan, oxaliplatin, and 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin combina tion chemotherapy in advanced colorectal carcinoma: a phase II study. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2002 Aug;2(2):104-10. PubMed PMID: 12453325.
- Bano N, Najam R, Qazi F, Mateen A. Clinical Features of Oxaliplatin Induced Hypersensitivity Reactions and Therapeutic Approaches. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2016;17(4):1637-41. PubMed PMID: 27221832.
- Andriollo G, Urbani S, Buonomo A, Aruanno A, Nucera E. Rapid protocol for irinotecan desensitization: a case report and literature review. Allergo J Int. 2020 Dec;29(8):286-8.
- Cubero JL, Escudero P, Yubero A, Millán P, Sagredo MA, Colás C. Successful Desensitization to Irinotecan After Severe Hypersensitivity Reaction. J InvestigAllergolClinImmunol. 2016;26(5):314-316. PubMed PMID: 27763858.
- Castells M. Rapid desensitization for hypersensitivity reactions to medications. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2009 Aug;29(3):585-606. PubMed PMID: 19563999.
- Siena S, Glynne-Jones R, Adenis A, Thaler J, Preusser P, Aguilar EA, et al. Reduced incidence of infusion-related reactions in metastatic colorectal cancer during treatment with cetuximab plus irinotecan with combined corticosteroid and antihistamine premedication. Cancer. 2010 Apr 1;116(7):1827-37. PubMed PMID: 20143444.
- Çakmak ME, Kaya SB, Can Bostan Ö, ÖztürkAktas Ö, Damadoglu E, Karakaya G, et al. Successful desensitization with chemotherapeutic drugs: a tertiary care center experience. Eur Ann Allergy ClinImmunol. 2022 Mar;54(2):90-94. PubMed PMID: 33944541.
- Rosique-Robles D, Vicent Verge JM, Borrás-Blasco J, Giner-Marco V, Casterá E, Galan-Brotons A, et al. Successful desensitization protocol for hypersensitivity reactions caused by oxaliplatin. Int J ClinPharmacolTher. 2007 Nov;45(11):606-10. PubMed PMID: 18077926.
- Cernadas JR, Brockow K, Romano A, Aberer W, Torres MJ, Bircher A, et al. General considerations on rapid desensitization for drug hypersensitivity - a consensus statement. Allergy. 2010 Nov;65(11):1357-66. PubMed PMID: 20716314.
- Jansman FG, Sleijfer DT, de Graaf JC, Coenen JL, Brouwers JR. Management of chemotherapy-induced adverse effects in thetreatment of colorectal cancer. Drug Saf. 2001;24(5):353-67. PubMed PMID: 11419562.
- Castells MC, Tennant NM, Sloane DE, Hsu FI, Barrett NA, Hong DI, et al. Hypersensitivity reactions to chemotherapy: outcomes and safety of rapid desensitization in 413 cases. J Allergy ClinImmunol. 2008 Sep;122(3):574- 80. PubMed PMID: 18502492.
- Zweizig S, Roman LD, Muderspach LI. Death from anaphylaxis to cisplatin: a case report. Gynecol Oncol. 1994 Apr;53(1):121-2. PubMed PMID: 8175010.
- Castells Guitart MC. Rapid drug desensitization for hypersensitivity reactions to chemotherapy and monoclonal antibodies in the 21st century. J InvestigAllergolClinImmunol. 2014;24(2):72-9. PubMed PMID: 24834769.
- Alvarez-Cuesta E, Madrigal-Burgaleta R, Angel-Pereira D, Ureña-Tavera A, Zamora-Verduga M, Lopez-Gonzalez P, et al. Delving into cornerstones of hypersensitivity to antineoplastic and biological agents: value of diagnostic tools prior to desensitization. Allergy. 2015 Jul;70(7):784-94. PubMed PMID: 25832325.
- Lenz HJ. Management and preparedness for infusion and hypersensitivity reactions. Oncologist. 2007 May;12(5):601-9. PubMed PMID: 17522249.
- Gutierrez IG, Baeza ML, Prieto A, Tornero P. Desensitization to Cytostatic Drugs. J Aller ClinImmunol. 2018 Feb 1;141(2):AB38.
- Yoshida Y, Hirata K, Matsuoka H, Iwamoto S, Kotaka M, Fujita H, et al. A single-arm Phase II validation study of preventing oxaliplatin-induced hypersensitivity reactions by dexamethasone: the AVOID trial. Drug Des DevelTher. 2015 Nov 11;9:6067-73. PubMed PMID: 26648694.
- Breslow RG, Caiado J, Castells MC. Acetylsalicylic acid and montelukast block mast cell mediator-related symptoms during rapid desensitization. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2009 Feb;102(2):155-60. PubMed PMID: 19230468.
- Tamura H. Anaphylactic shock leading to cardiopulmonary arrest: case report. Reactions. 2015 May;1552:171-23.
- Wilke H, Glynne-Jones R, Thaler J, Adenis A, Preusser P, Aguilar EA, et al. Cetuximab plus irinotecan in heavily pretreated metastatic colorectal cancer progressing on irinotecan: MABEL Study. J ClinOncol. 2008 Nov 20;26(33):5335-43. PubMed PMID: 18854570.
- Ring J, Beyer K, Biedermann T, Bircher A, Fischer M, Fuchs T, et al. Guideline (S2k) on acute therapy and management of anaphylaxis: 2021 update. Allergo J Int. 2021;30(1):1-25. PubMed PMID: 33527068.
- Choo KJ, Simons E, Sheikh A. Glucocorticoids for the treatment of anaphylaxis: Cochrane systematic review. Allergy. 2010 Oct;65(10):1205-11. PubMed PMID: 20584003.
- Alqurashi W, Ellis AK. Do Corticosteroids Prevent Biphasic Anaphylaxis? J Allergy ClinImmunolPract. 2017 Sep-Oct;5(5):1194-1205. PubMed PMID: 28888249.
- Thomas RR, Quinn MG, Schuler B, Grem JL. Hypersensitivity and idiosyncratic reactions to oxaliplatin. Cancer. 2003 May 1;97(9):2301-7. PubMed PMID: 12712487.
- Nisi C, Moretti A, Donati D, Carandina I, Da Ros L, Bannò E, et al. E18A post-reaction regimen for CRC patients manifesting hypersensitivity to oxaliplatin: an effective alternative not to rule out an important option of treatment. Ann Oncol. 2015;26:41.
- Santini D, Tonini G, Salerno A, Vincenzi B, Patti G, Battistoni F, et al. Idiosyncratic reaction after oxaliplatin infusion. Ann Oncol. 2001 Jan;12(1):132- 3. PubMed PMID: 11249043.
- Madrigal-Burgaleta R, Berges-Gimeno MP, Angel-Pereira D, Ferreiro-Monteagudo R, Guillen-Ponce C, Pueyo C, et al. Hypersensitivity and desensitization to antineoplastic agents: outcomes of 189 procedures with a new short protocol and novel diagnostic tools assessment. Allergy. 2013 Jul;68(7):853- 61. PubMed PMID: 23647576.
- Mueller HL. Insect allergy.PediatrClin North Am. 1959;6:917-952.
- Ring J, Messmer K. Incidence and severity of anaphylactoid reactions to colloid volume substitutes. Lancet. 1977 Feb 26;1(8009):466-9. PubMed PMID: 65572.
- Bakiri A,Mingomataj EÇ.The significance of absent skin symptoms during severe anaphylaxis.Ann ClinExpImmunol. 2021;3:4.
- Bakiri AH, Gurakuqi-Qirko A, Mingomataj DÇ, Luku D, Rudzeviciene O, Mingomataj EÇ. From the lack of skin symptoms to the shortening of the latency interval – An attempt to include warning signals for severe anaphylaxis in a severity assessment tool. Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2021;6:1-7.
- Asare K. Diagnosis and treatment of adrenal insufficiency in the critically ill patient. Pharmacotherapy. 2007 Nov;27(11):1512-28. PubMed PMID: 17963461.